🏠
🕯 Overview of Slides
- What is C?
- Syntax
- Type System
- Number Systems Review
- Variables in Memory
- Arrays and Pointers
- Strings
- Stack and Heap
- Avoiding Trouble with Memory
- Structs
- Function Pointers and Object-Oriented C
-
Code Sources
🔦 What is C?
- Dennis Ritchie at AT&T Bell Labs in 1972
- Speedcode -> FORTRAN -> ALGOL 58 -> ALGOL 60 -> CPL -> BCPL -> B -> C
- Influenced countless languages, including: C++, C#, Java, Python, Go, and Obj-C
- Low-level systems language
- Static type system with weak enforcement
- Architecture-specific language -- not WORA
- C source files are compiled to object files
- Programs and libraries
🌅 Hello World
- #include preprocessing directives
- .c and .h files
- for, if, {}, quotes, and ;
- <stdio.h>
- Return success value
🚌 Basic Types
- char, int, float and double
- Modifiers: signed, unsigned, short, and long
-
Summary of types
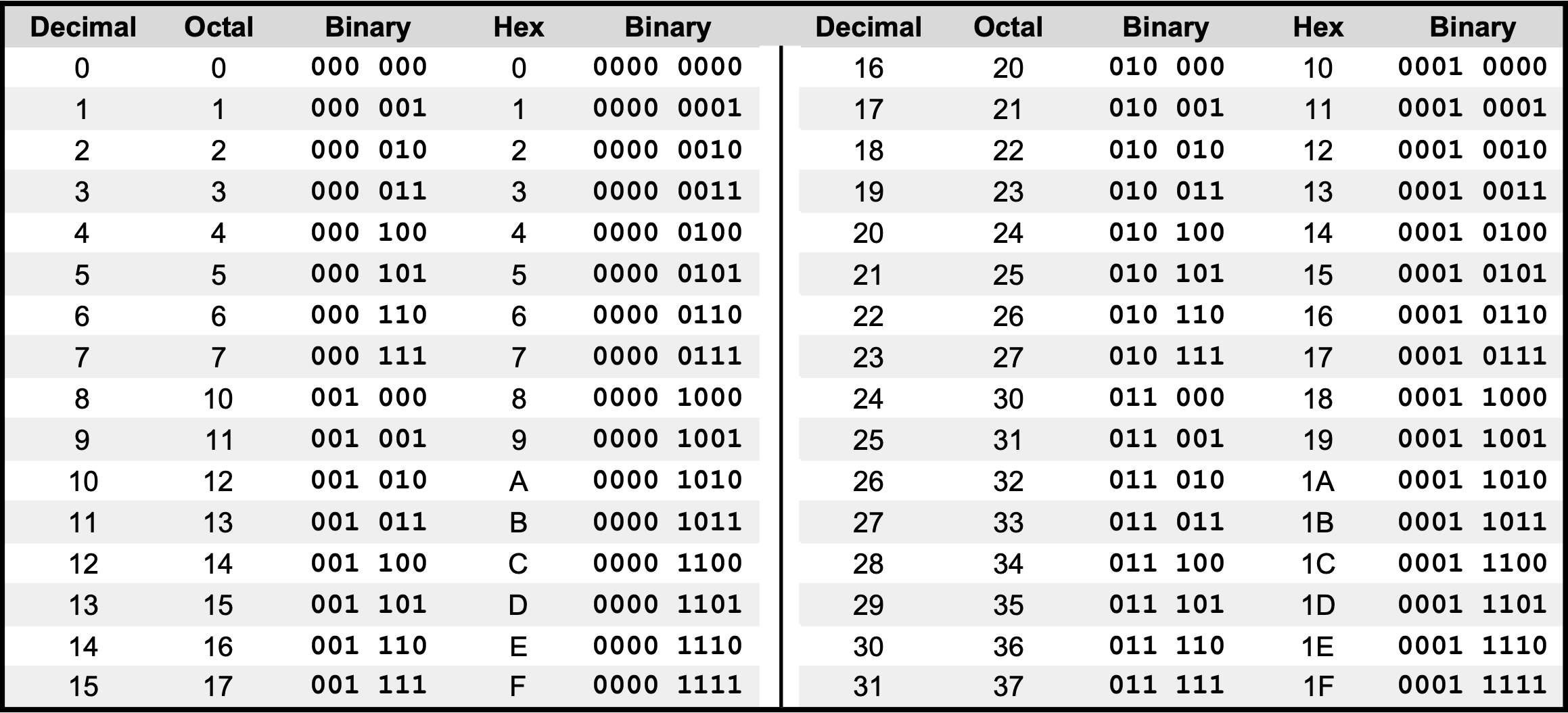
🧮 Decimal, Octal, Hex, and Binary
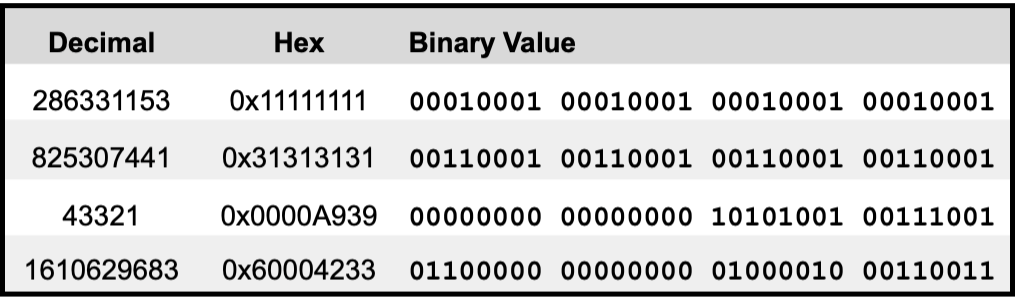
📬 Hex Addresses
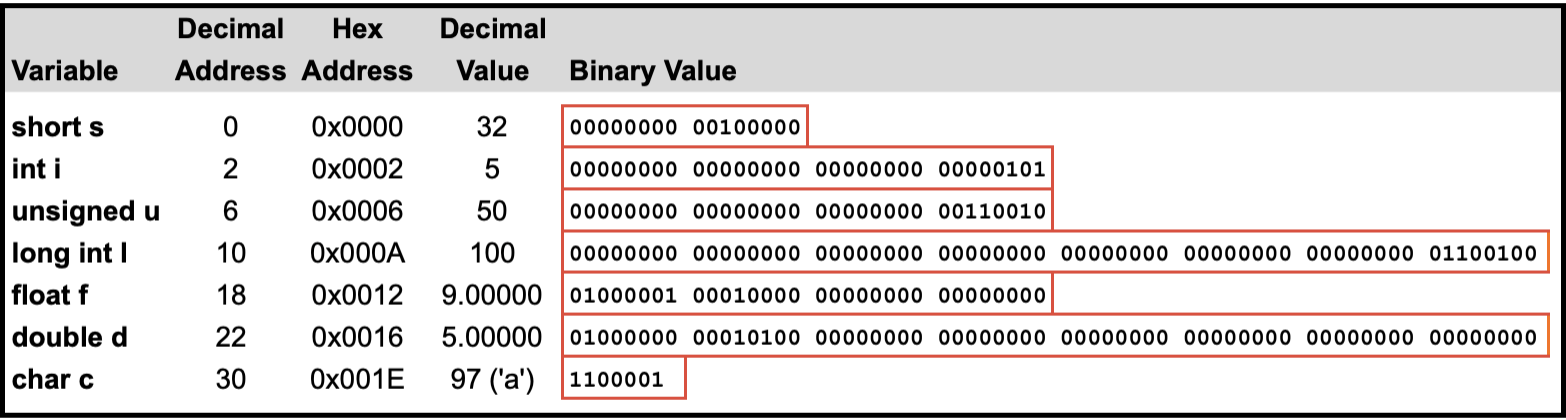
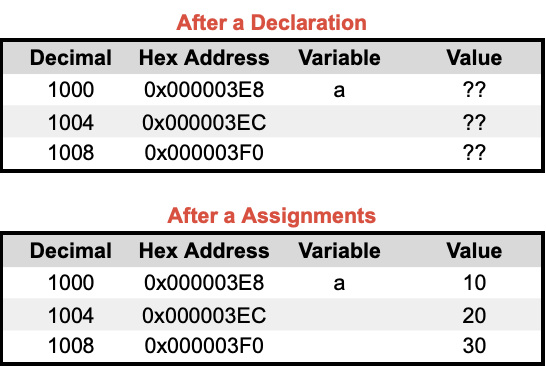
🔬 Variables in Memory
🔬 Arrays in Memory
🔬 Arrays in Memory
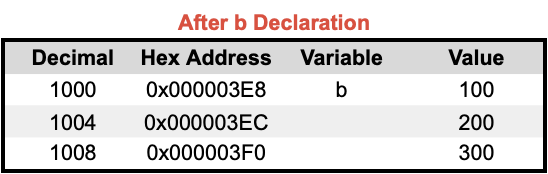
🔬 Pointers in Memory
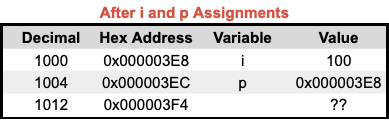
🔬 Pointers in Memory
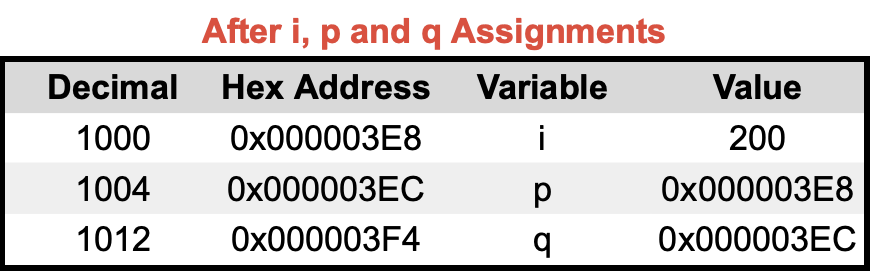
📱 Call by Value and Reference
🔬 Pointers to Arrays in Memory
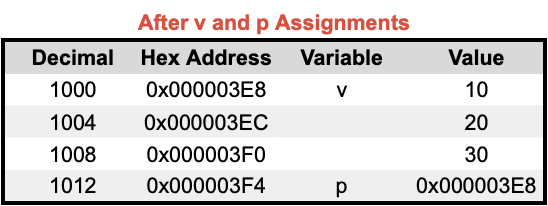
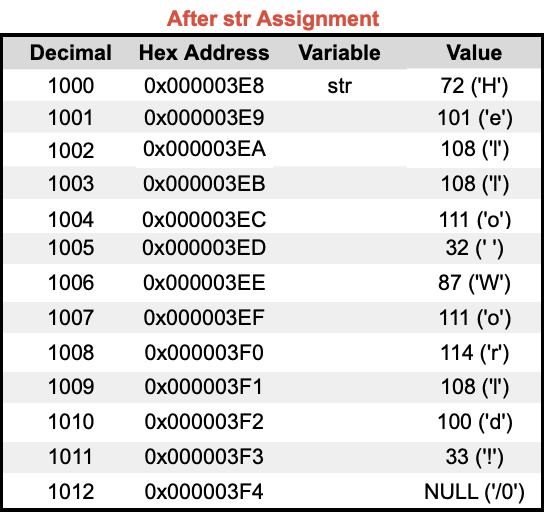
🔬 Strings in Memory
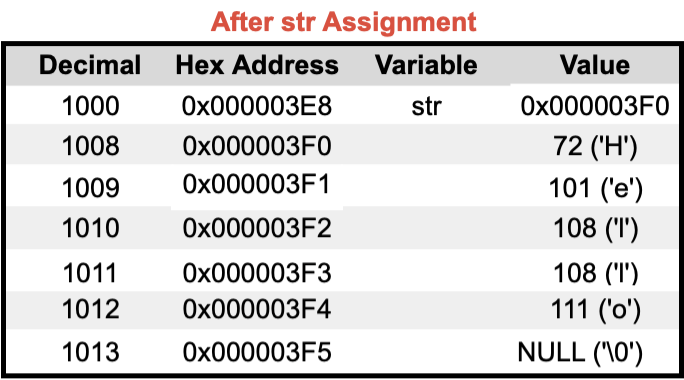
🔬 Strings in Memory
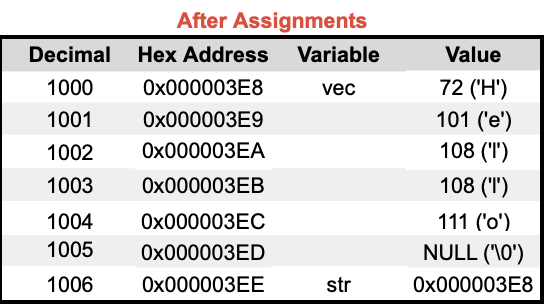
🔬 Strings in Memory
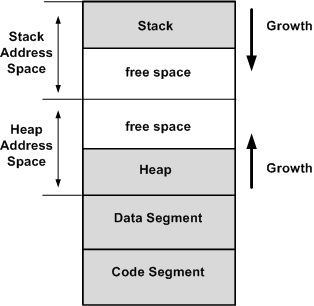
The Stack and Heap
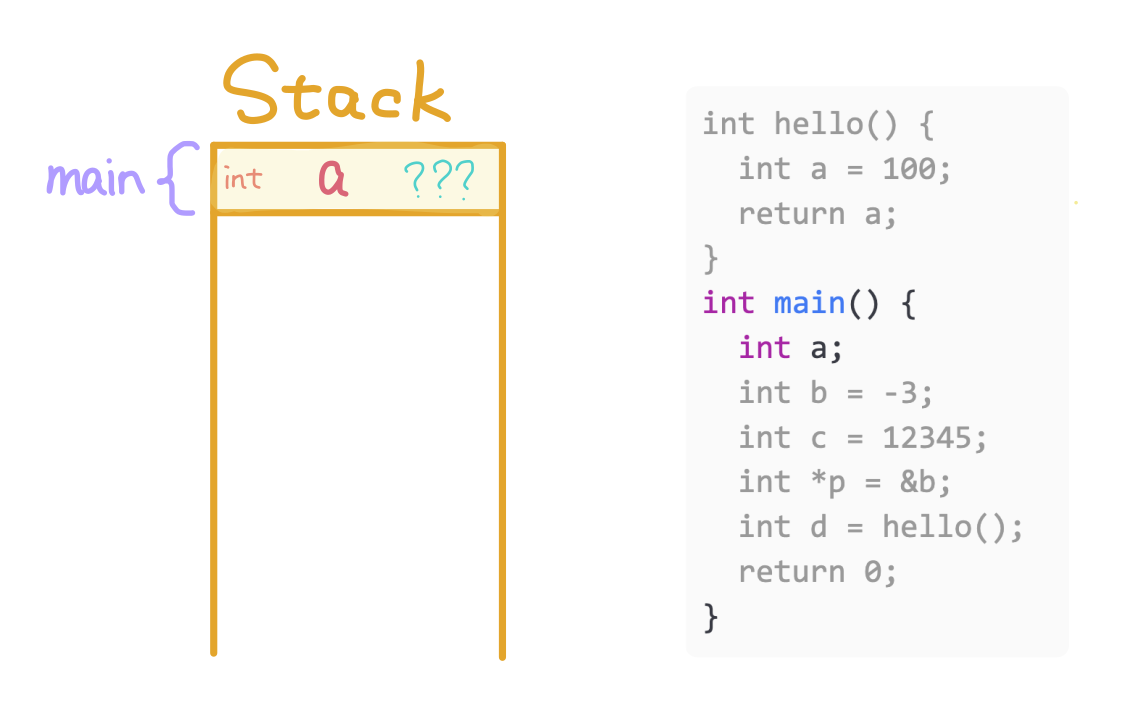
Allocate variable a for main
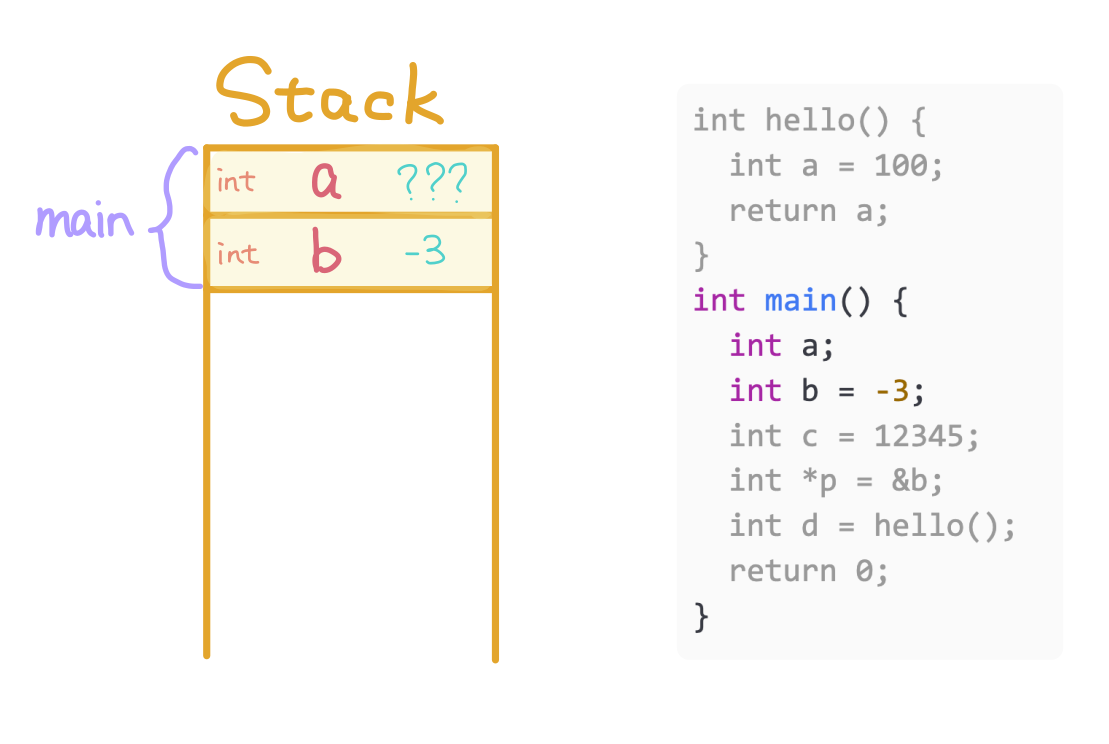
Allocate b for main and store -3
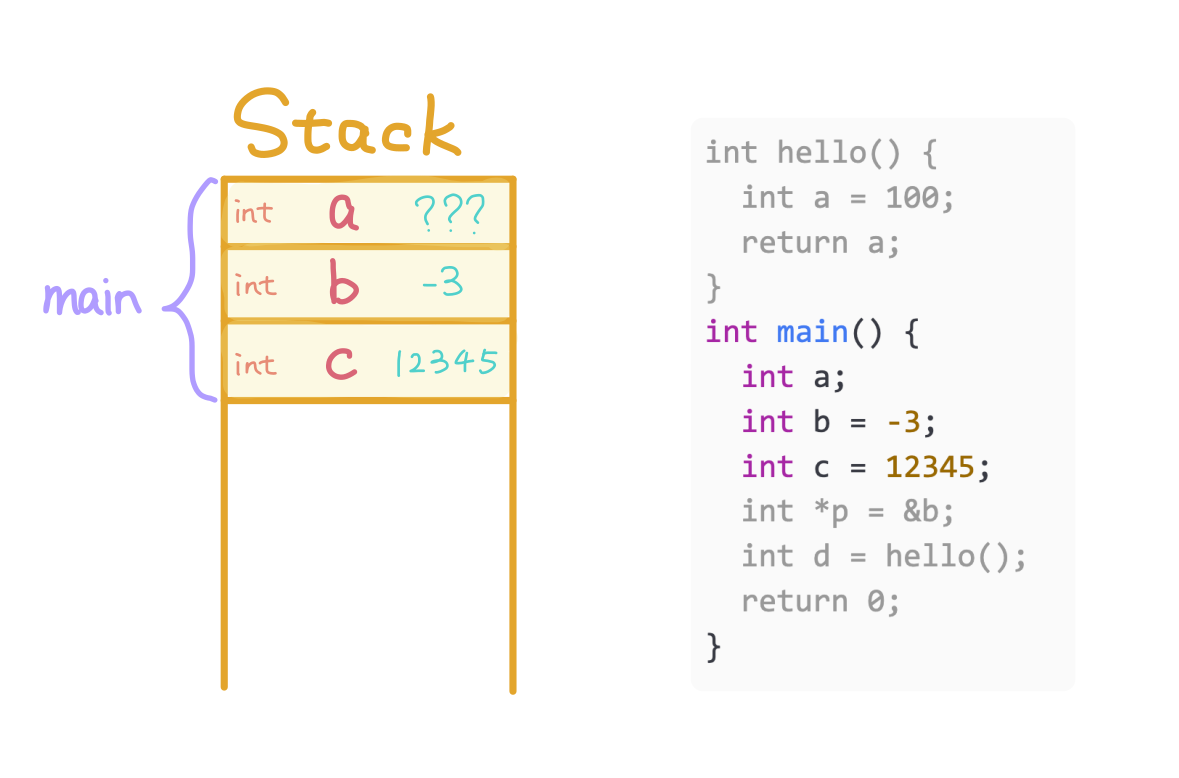
Allocate c for main and store 12345
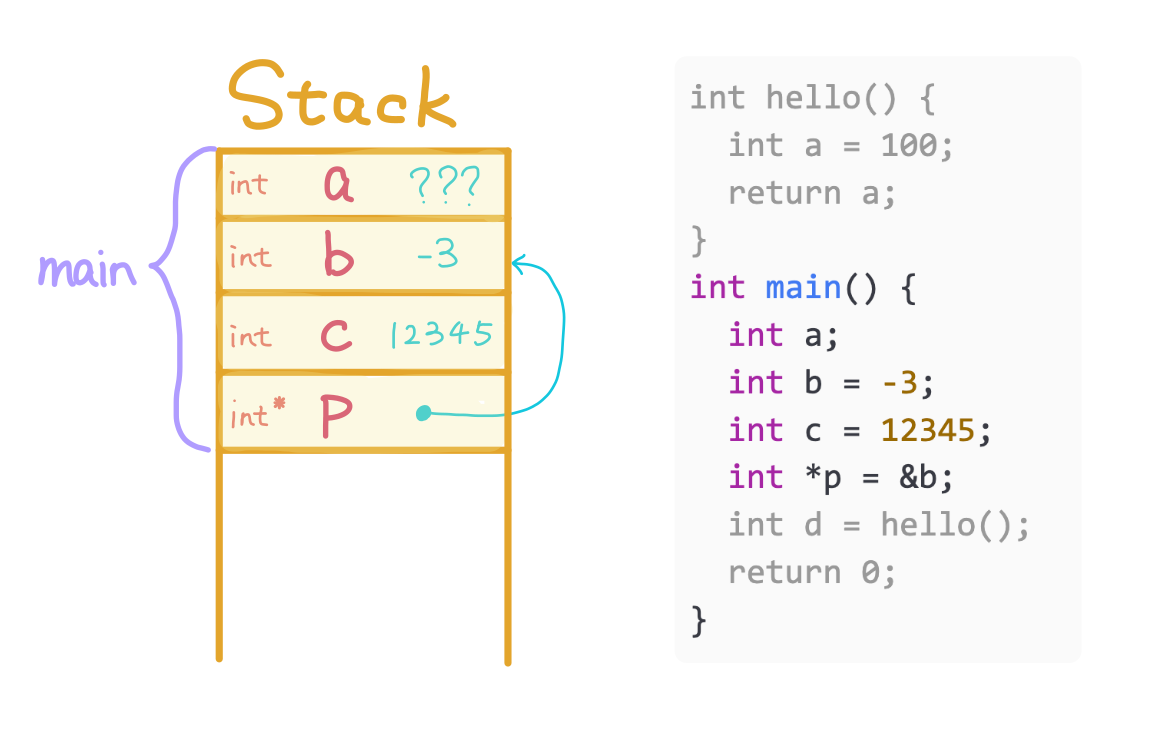
Allocate p for main and store address of b
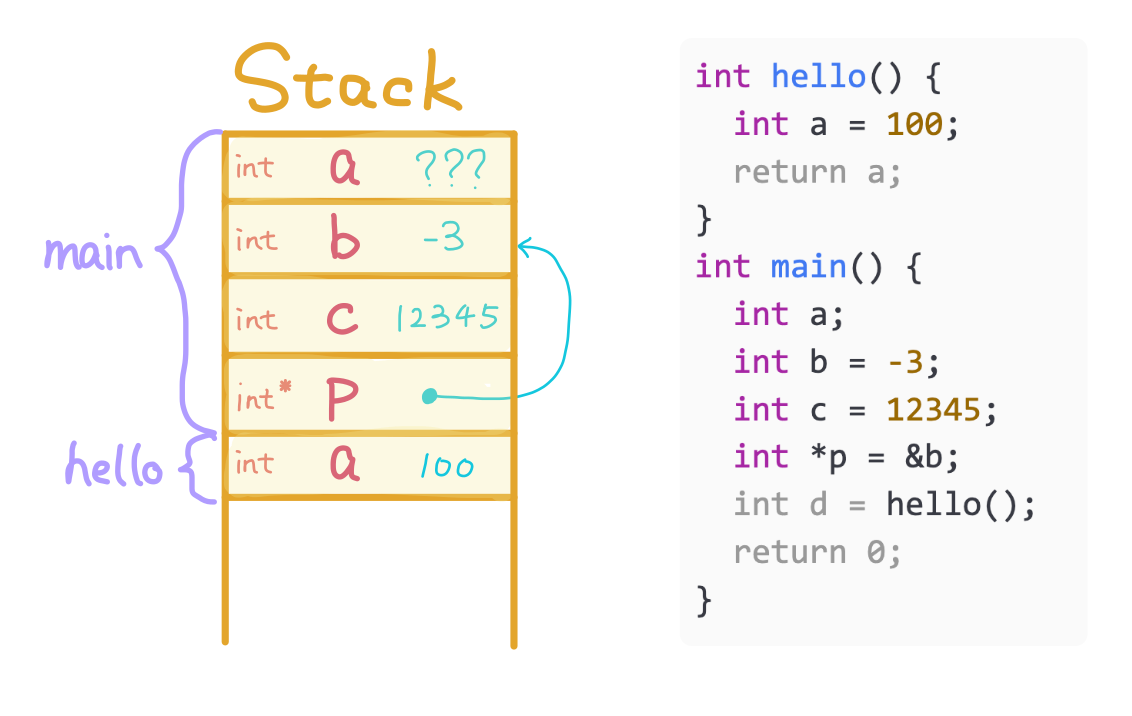
Allocate variable a for hello and store 100
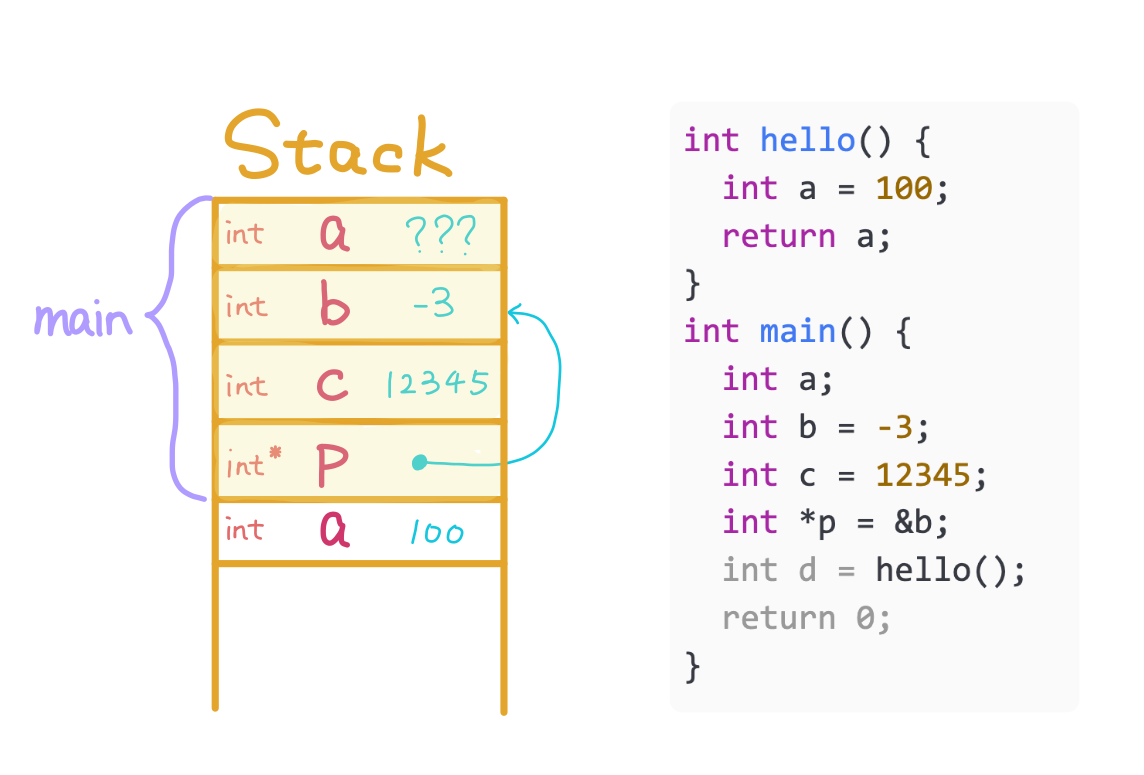
Deallocate the stack memory of hello and return 100 to main
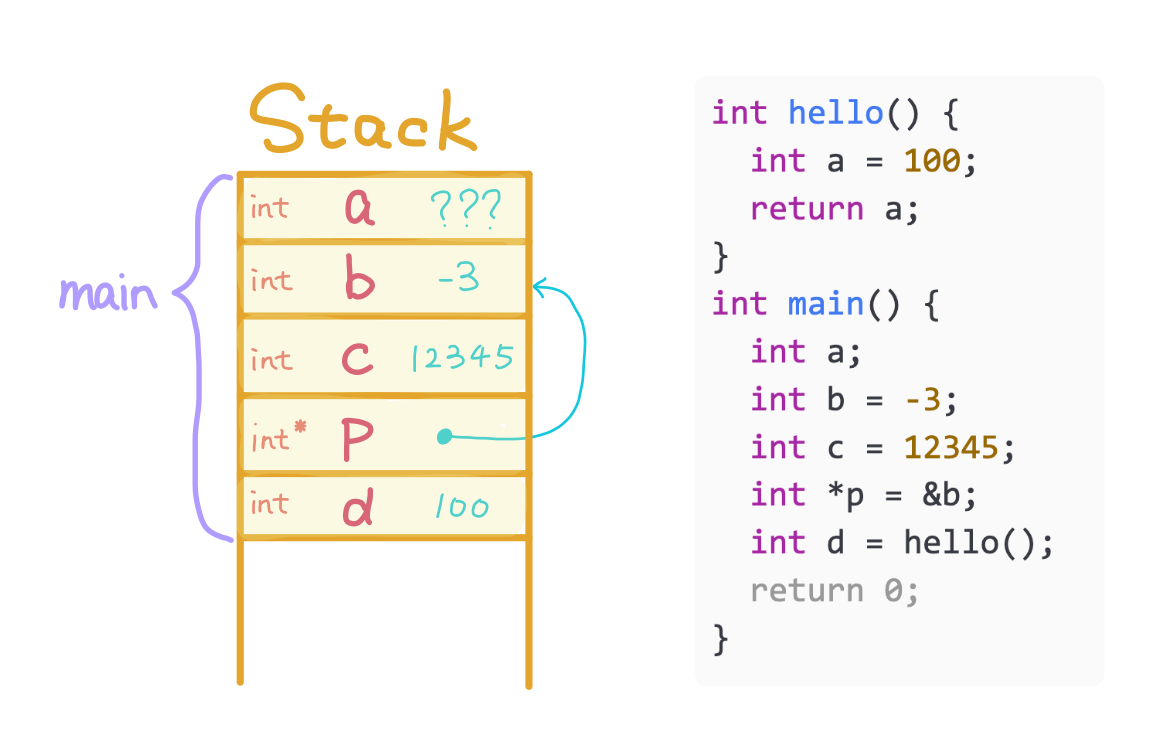
Allocate d for main and store 100
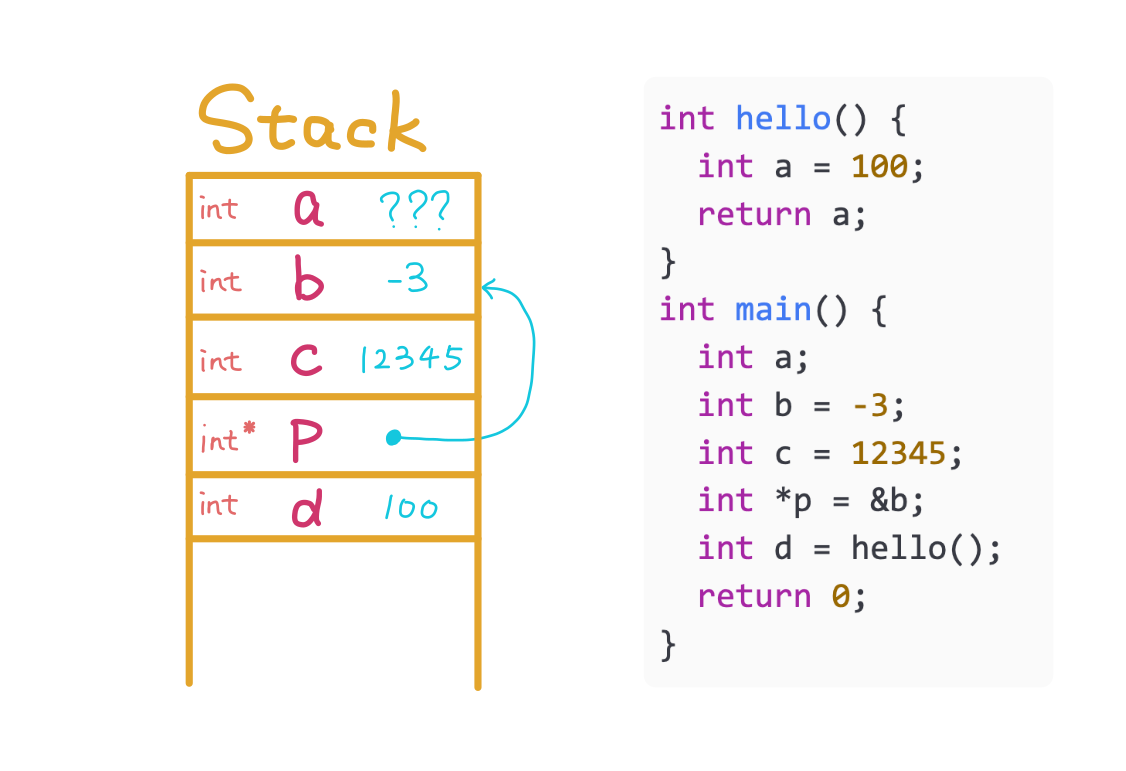
Deallocate the stack memory of main and return 0
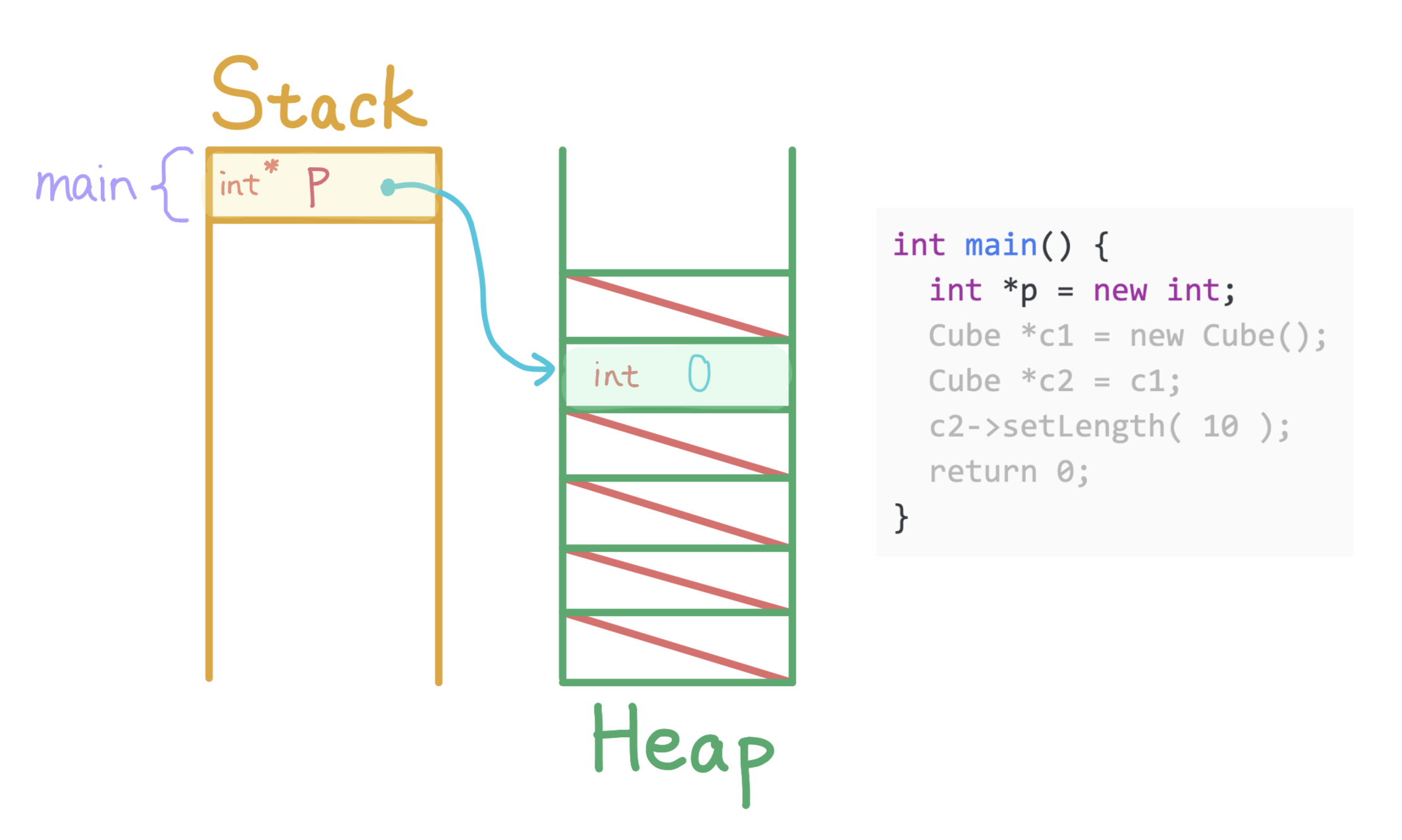
Allocate an integer with default value 0 on the heap, allocate p on main's stack to store the address of the integer
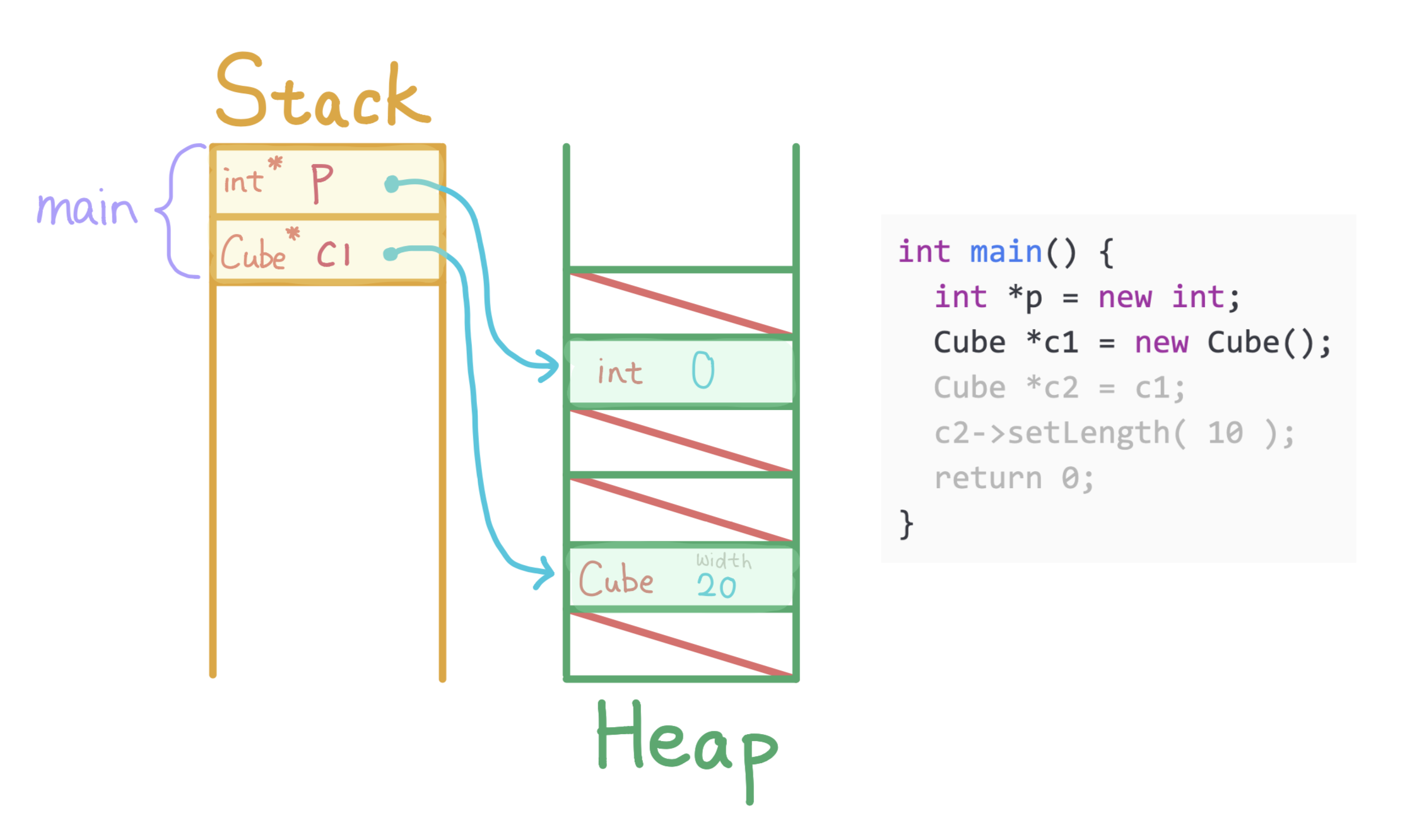
Allocate a Cube with default width 20 on the heap, allocate c1 on main's stack to store the address of the Cube
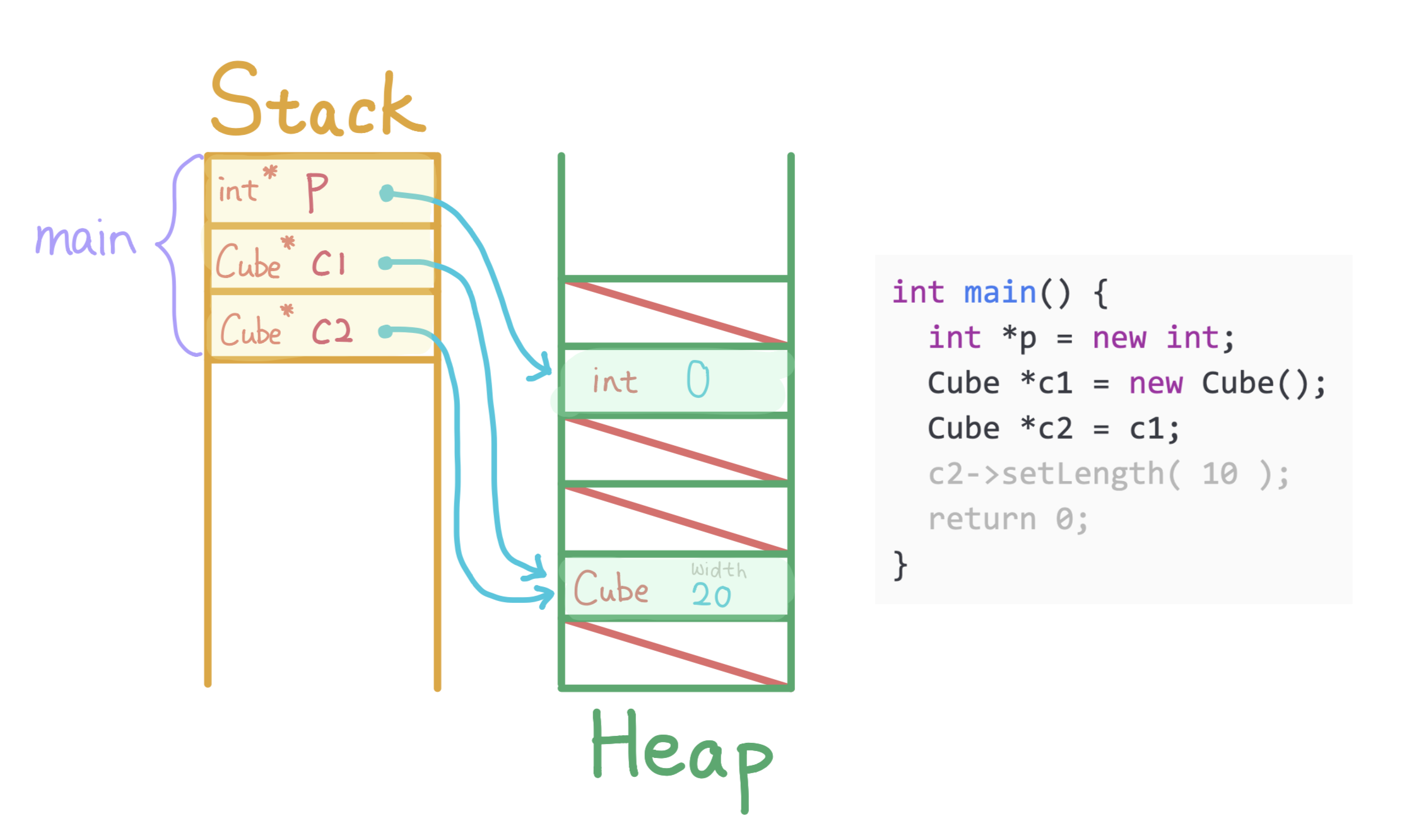
Allocate c2 on main's stack and store a copy of c1
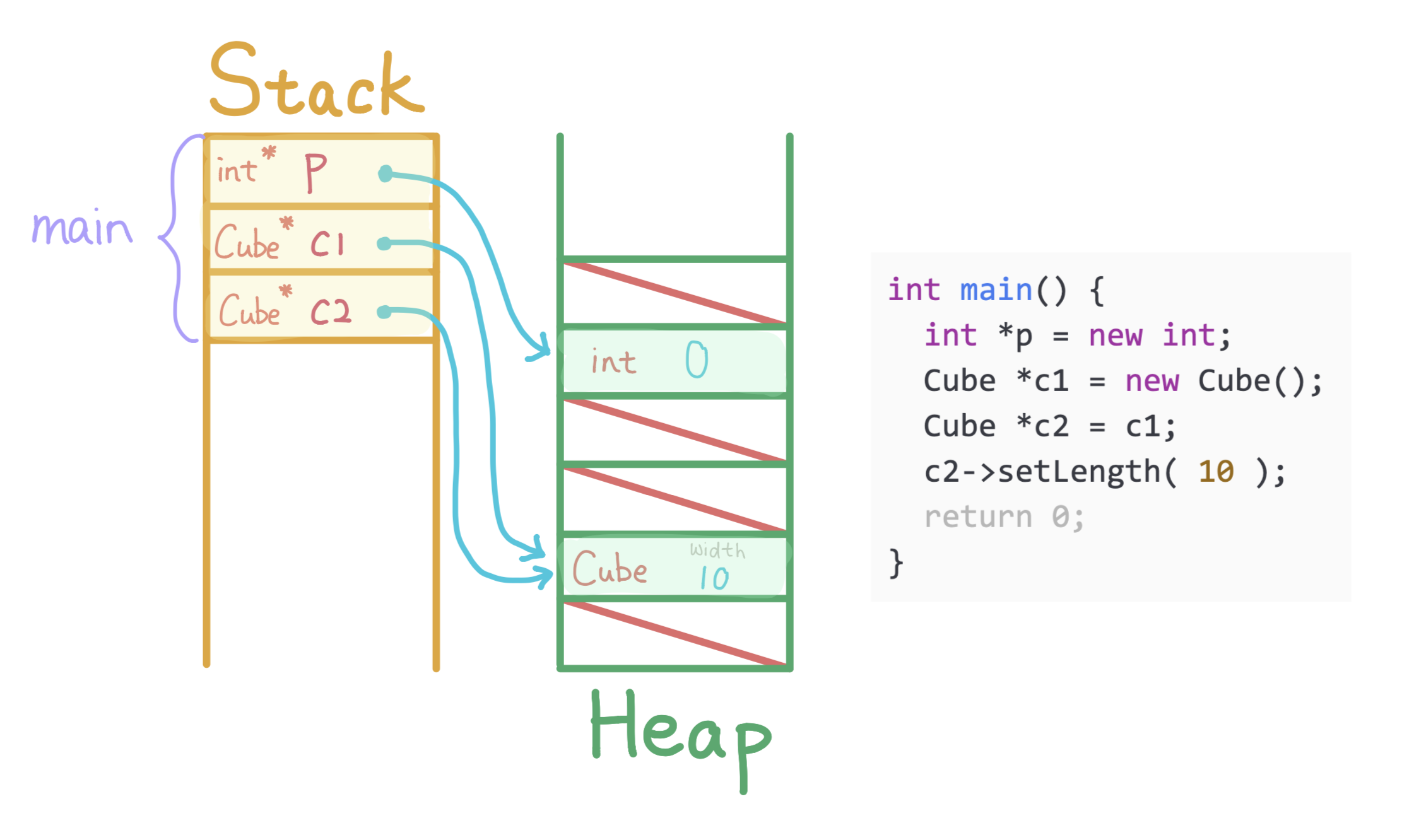
Call method setLength on c2, changes the width of the Cube pointed by both c1 and c2
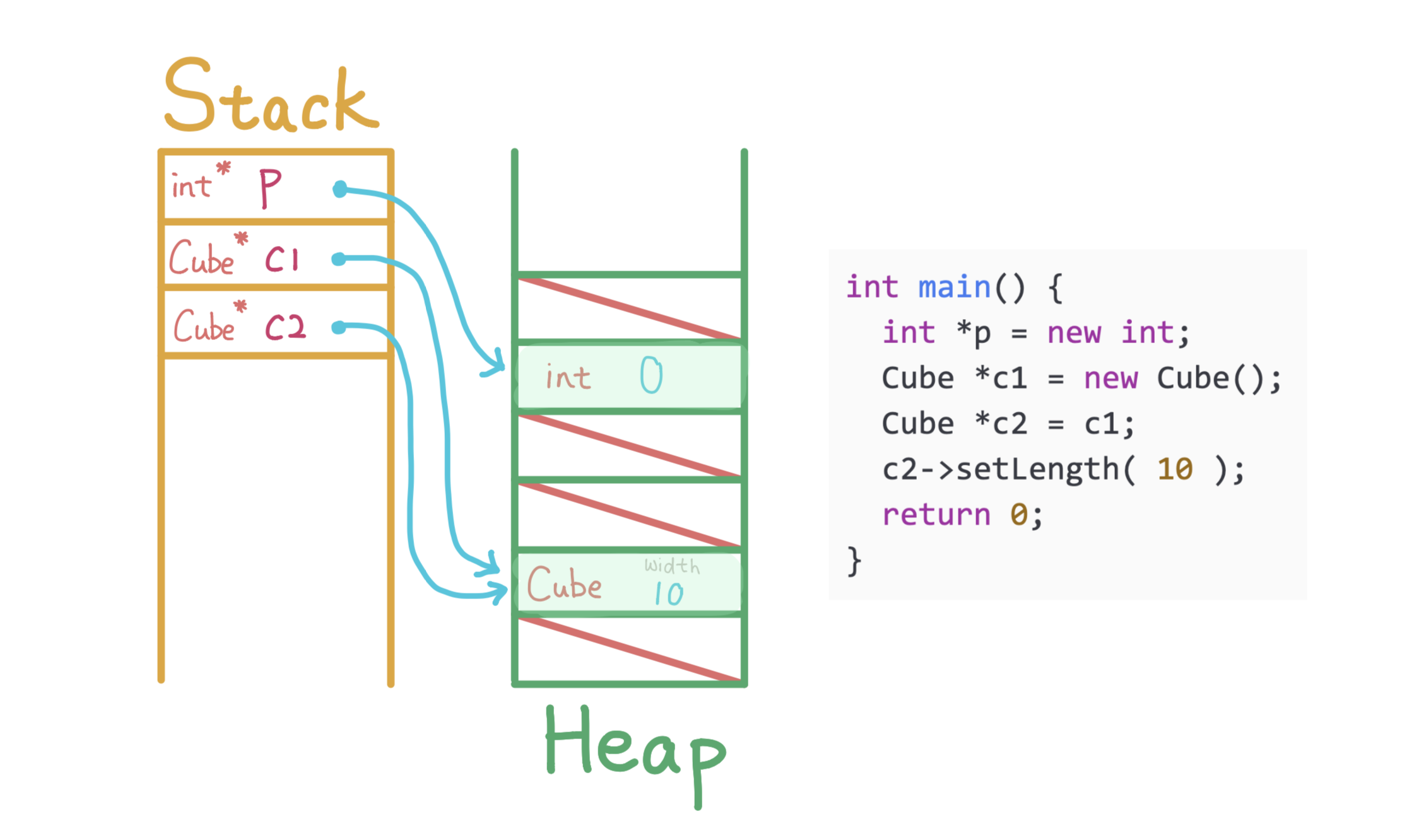
Deallocate stack memory of main and return 0
🔬 malloc() Memory
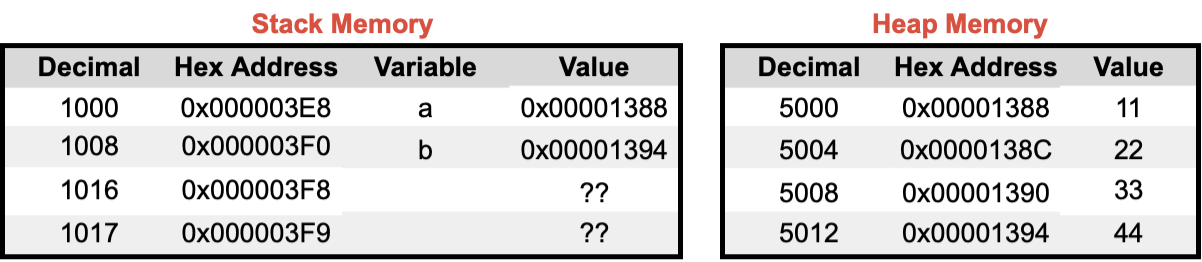
⛰ Initialized Heap Memory
🔁 Reallocating Heap Memory
⚠ Avoiding Trouble with Memory
🔬 String Array in Memory

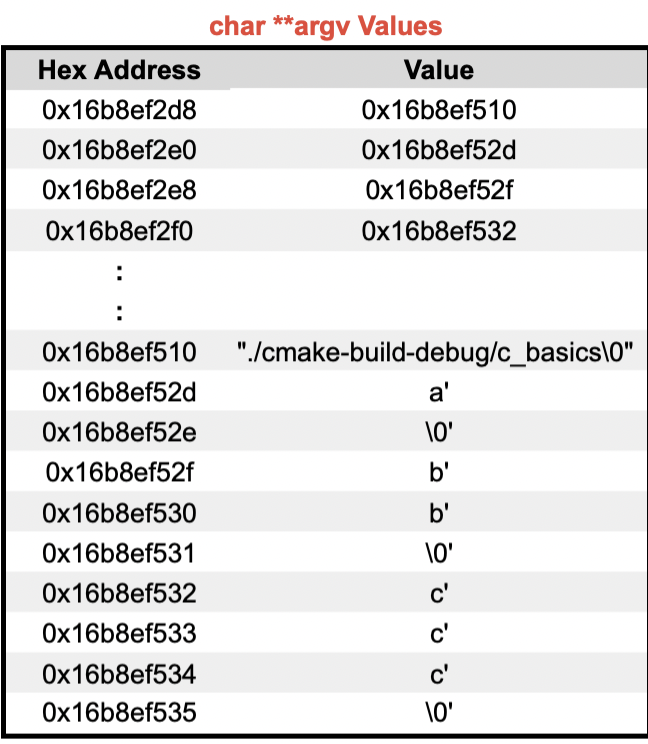
👉 Higher Order Functions (1)
👉 Higher Order Functions (2)
🏦 Understanding Exploits
 https://pambrose.github.io/myslides/c.html
https://pambrose.github.io/myslides/c.html



























